






As a form of seaming, welding technology has existed for centuries. Currently, there are about 100 welding methods used in different industry sectors. The use of industrial gases (whether using separate or mixed gases) to optimize the welding process dates back to the 1940s and 1950s. Since then, the gas welding process has become the most important method in the welding process. Important gas-shielded welding methods include gas metal arc welding, metal active gas shielded welding, inert gas tungsten arc welding, and plasma welding. The 80s and 90s of the 20th century witnessed a number of innovations in welding processes. Including laser welding, tandem welding and laser hybrid welding.
A deep understanding of the "internal composition" of gases and the interaction of their constituents in a mixed state is critical in the successful application of gas welding. The welding arc itself is a highly efficient but complex tool with a large amount of ionized gas and metal vapor, which means that the physical properties of the gas have a direct and immediate effect on the arc. In addition, the process gas also contacts the hot metal, which is a highly active region, and the chemical and metallurgical effects of the gas also play an important role. Shanghai has a suitable solution for your welding needs.
Cutting
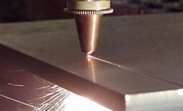
In the case of oxyfuel combustion, plasma and laser cutting, thermal energy is used to cauterize the material to a temperature at which it burns, melts or evaporates. Pure oxygen combustion cutting and oxygen-consuming laser cutting utilize the heat generated by the oxygen reaction during operation. The flame and laser beam only burn the material to the point of ignition. The oxygen nozzle ablates the material and then blows off the melt and residue. The cutting speed depends on the purity of the oxygen and the shape of the cutting gas nozzle. In plasma cutting and laser cutting using nitrogen, the material is cauterized to a melting temperature, and the cutting gas blows out the slag. The nature of the cutting gas needs to be adjusted to get the best results.
Lasers can also be used to vaporize materials. In the case of vaporized metal materials, laser drilling or perforation can be performed. During the drilling process, the gas can inhibit the flammability of the material and aid in the removal of the material.
As a high-precision technology, laser cutting has a very high requirement for gas quality and purity (He~5.0 N2~5.0 CO2~4.5). Shanghai Chen's laser gas series can meet the requirements of various laser cutting machines. Learn more about linking gas mixtures.
网站客服咨询客服
热线电话:
021-52961966
